Fubang is a professional manufacturer specializing in the design, production and sales of stainless steel chains.
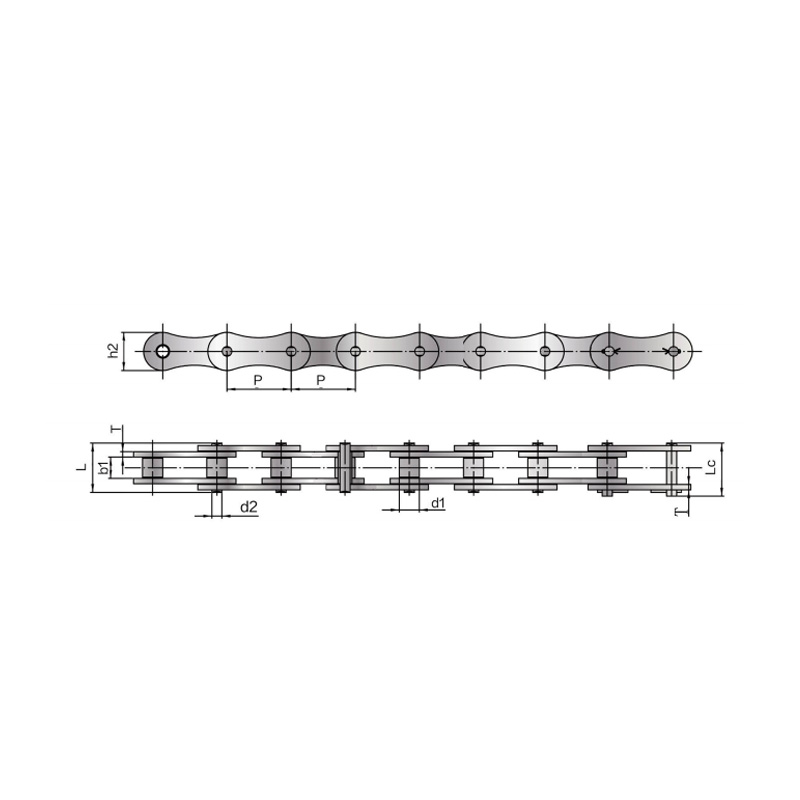
Our A series short pitch precision roller chains comply with various international standards and are...
See DetailsDriving chain is essential components in various machinery, including motorcycles, bicycles, industrial equipment, and agricultural machines. They transmit power efficiently between two rotating shafts, ensuring smooth operation. However, choosing the right chain and maintaining it properly can significantly impact performance and longevity.
This guide covers everything you need to know about driving chains, including types, common issues, maintenance tips, and how to select the best one for your needs.
Driving chains come in different designs, each suited for specific applications. Below is a comparison of the most common types:
| Chain Type | Description | Common Uses |
| Roller Chain | Features cylindrical rollers for smooth engagement with sprocket teeth. | Bicycles, motorcycles, industrial machinery. |
| Silent Chain | Also known as inverted tooth chains, they operate quietly with minimal noise. | Automotive engines, high-speed drives. |
| Timing Chain | Synchronizes engine valve and piston movement for precise timing. | Internal combustion engines. |
| Leaf Chain | Consists of link plates without rollers, designed for high tensile strength. | Forklifts, lifting equipment. |
Each type has unique advantages, so selecting the right one depends on factors like load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions.
Even the best-quality chains can develop problems if not properly maintained. Here are some frequent issues and their causes:
Addressing these issues early can prevent costly repairs and downtime.
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of a driving chain and ensures optimal performance. Follow these steps:
Selecting the right chain involves considering several factors:
Here’s a quick reference table for chain selection:
| Factor | Consideration |
| Load Capacity | Choose a chain rated for higher than the expected load. |
| Speed | High-speed applications need precision-engineered chains. |
| Environment | Use corrosion-resistant materials in harsh conditions. |
| Maintenance Needs | Some chains require frequent lubrication, while others are self-lubricating. |
Even with proper maintenance, chains wear out over time. Look for these signs:
Visible wear on rollers and pins
Chain elongation beyond 1-2% of original length
Rust or cracks in the links
Frequent slippage or unusual noises
Replacing a worn chain prevents further damage to sprockets and other components.
Driving chains play a crucial role in power transmission across various machines. Understanding the different types, maintenance practices, and selection criteria ensures optimal performance and longevity. Regular inspection and proper care can save time and money while preventing unexpected breakdowns.
By following this guide, you can make informed decisions about driving chains, whether for industrial, automotive, or personal use. If you found this article helpful, share it with others who might benefit from this information!